Accessibility & GenAI
Accessibility in higher education is essential for fostering an inclusive academic environment, ensuring all students, including those with disabilities, have equal access to learning experiences, resources, and environments. This commitment aims to remove barriers that might impede full participation in educational activities.
Technology has historically been instrumental in enhancing accessibility within educational settings. Assistive technologies such as screen readers and adaptive learning platforms have significantly contributed to creating inclusive educational experiences.
AI-powered tools like Grammarly and Microsoft Office have already made strides in supporting writing and presentation tasks. They assist with grammar, sentence structure, and readability. These AI applications not only enhance the quality of written work but also contribute to making educational content more accessible and understandable to a broader audience. UNESCO has recognised the potential of AI to contribute significantly towards achieving Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG 4), which aims to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all.
Practical Examples of AI in Accessibility
When it comes to GenAI there are practical ways in which it can make access to education more accessible.
Translating and Summarising Information:
GenAI tools have the capability to translate content into various languages, ensuring students from diverse linguistic backgrounds can access information in multiple languages. Additionally, these tools can succinctly summarise complex materials, making intricate subjects more digestible and accessible. In the image below, a photo from an iphone camera has been uploaded to ChatGPT, ChatGPT then translates the content and explains it.

Simplifying Complex Content:
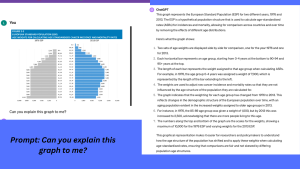
GenAI has the capability to break down advanced or specialised concepts into more digestible forms, making it particularly useful for students who may find the original content overwhelming. This includes the ability to explain intricate graphs and data, ensuring that all students can grasp the underlying concepts without being hindered by the complexity of the presentation. In the graph below an image(Source: National Cancer Registry of Ireland Stastical Report 2022, Pg 13) has been put into the ChatGPTPrompt and on the right you can see the output explaining the graph.
Clarifying Terms and Concepts
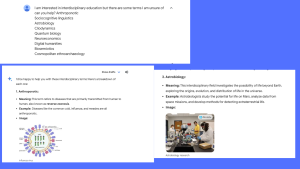
GenAI can serve as an on-demand tutor, providing clear and concise explanations for challenging terms and concepts. This instant clarification helps in demystifying subject matter that students might otherwise find perplexing.
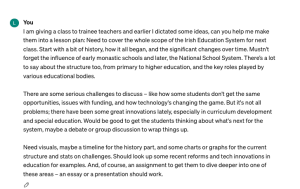
Organising Thoughts into Coherent Output:
Organising Thoughts into Coherent Output: Many students and academics grapple with organising their ideas effectively. GenAI can take disorganised thoughts and transform them into well-structured arguments or narratives, thereby streamlining the writing process. For instance, dictating fragmented ideas into a programme like Microsoft Word and employing AI to refine these into a coherent piece of writing can be particularly useful.

Time Management:
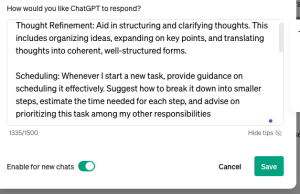
Task initiation and organisation are common challenges, especially for neurodivergent students. AI can offer structured plans and prompts, acting as a virtual organiser that guides the user through initiating and systematically tackling tasks. One way in which this could be used is through custom instructions. Custom instructions are prompts which will always guide the AI, for example you could put anything you find challenging in the custom instructions and ChatGPT will consider it in it’s responses.
In this video you will find some guidance on using AI with neurodivergent students:
Considerations for AI & Accessibility
The Need for Formal Recognition and Research
The exploration of AI’s role in education and to promote accessibility, particularly for individuals with ADHD, highlighted the need for nuanced understanding of its benefits and challenges. Melo’s (2023) insights into ChatGPT’s function as an assistive tool for individuals with ADHD reveal the potential for AI to create more focused and streamlined learning experiences. This underscores the necessity for formal recognition and in-depth research to fully appreciate and utilise AI’s educational capabilities.
Concurrently, Wallbank (2023) raises concerns about the rapid proliferation of AI tools in higher education. While these tools offer substantial support for various academic tasks, their abundance could overwhelm students with ADHD, leading to cognitive overload and a disjointed learning process. This paradox highlights the critical need for a balanced perspective on AI’s educational integration, acknowledging its potential to enhance learning while being cognisant of its ability to complicate traditional learning mechanisms. It is imperative for the educational community to continually engage in research and dialogue to navigate these complexities effectively, ensuring AI’s incorporation is both beneficial and considerate of its impact on student focus and participation.
Addressing Accessibility and Cost Concerns
Barriers like the cost of technology, internet access, and digital literacy overlap with traditional barriers to assistive technologies. Universities must strategies to ensure students are not disadvantaged and access to these tools is equitable.
Encouraging Open Discussions and Acknowledgment
For AI to fully serve as an assistive technology, open discussions within the educational community are vital. Acknowledging AI’s role and exploring its applications can lead to more inclusive and accessible learning environments. This process involves not just recognising AI’s capabilities but actively integrating it teaching and learning and discussions about inclusivity and accessibility.
References:
Melo, M. (2023). CHATGPT can help students and faculty with ADHD (opinion). Retrieved from https://www.insidehighered.com/views/2023/03/01/chatgpt-can-help-students-and-faculty-adhd-opinion.
Wallbank, A., (2024). ADHD in higher education: Is Digital Learning making it worse? Retrieved from https://www.timeshighereducation.com/campus/adhd-higher-education-digital-learning-making-it-worse.

