Research & AI in Higher Education
While this guide primarily addresses teaching and learning, it’s important to acknowledge AI’s emerging role in academic research. AI-powered tools are also going to have potential impact in research with tools claiming to enhance efficiency in data collection, analysis, and interpretation. However, as noted throughout such advancements should not compromise research quality or reliability. This section doesn’t endorse specific tools but aims to inform educators about their potential research applications.
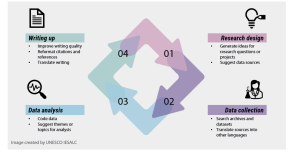
AI Research tools:

